27 Terrifying Ransomware Statistics & Facts You Need To Read
Ransomware is a form of malware or a virus that prevents users from accessing their systems or data until a sum of money is paid.
Clicking on infected links is still a primary way for cybercriminals to deliver their payloads. Ransomware was the most significant malware threat of 2018, with numerous high profile ransomware attacks. These malicious attacks show no signs of slowing in 2019.
Only with a proactive disaster recovery plan can increase your chances of withstanding a ransomware attack.
Let’s look at the staggering facts.
50% of a surveyed 582 cybersecurity professionals do not believe their organization is prepared to repel a ransomware attack. (Source: Pwnie Express)
Ransomware costs businesses more than $75 billion per year. (Source: Datto)
The average cost of a ransomware attack on businesses was $133,000. (Source: Sophos)
75% of companies infected with ransomware were running up-to-date endpoint protection. (Source: Sophos)
Want to learn the key tactics to preventing and detecting ransomware attacks? Read This.
Rate Of Ransomware Attacks
- A new organization will fall victim to ransomware every 14 seconds in 2019, and every 11 seconds by 2021. (Source: Cyber Security Ventures)
- 1.5 million new phishing sites are created every month. (Source: webroot.com)
- Ransomware attacks have increased over 97 percent in the past two years. (Source: Phishme)
- A total of 850.97 million ransomware infections were detected by the institute in 2018.
- 34% of businesses hit with malware took a week or more to regain access to their data. (Source: Kaspersky)
- In 2019 ransomware from phishing emails increased 109 percent over 2017. (Source: PhishMe)

Statistics on Ransom Demands
Ransomware financial demands are often severe and significant.
Ransomware Statistics show that hackers are focusing more steadily on large businesses who will often pay tens of thousands of dollars to receive their data back.
- An IBM study suggested that over a quarter of all companies would pay more than $20,000 to hackers to retrieve data that had been stolen.
- Ransomware generates over $25 million in revenue for hackers each year. (Source: Business Insider)
- The NotPetya ransomware attack cost FedEx $300 million in Q1 2017. (Source: Reuters)
- More than half of ransoms were paid bitcoin.
- The average ransom demand increased in 2018 to $1,077.
- Ten percent of all ransom demands are over $5,000. (Source: Datto)
- Fewer than a third of organizations who pay the ransom receive all of their money back. (Source: Courant
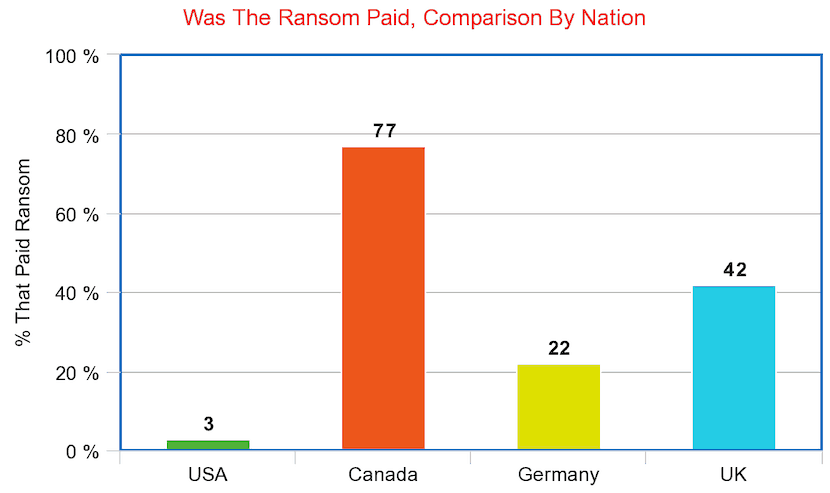
- 97% of United States’ companies refused to pay a ransom. 75% of Canadian companies paid, followed by, 22% of German businesses, and 58% in the UK.
Facts on The Biggest Ransomware Attacks of 2018
Recent ransomware attacks in 2018 crippled businesses large and small. Here is an insight into just a few high profile cases.
TSMC
A new variant of WannaCry ransomware wreaked havoc with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) this summer.
The manufacturer was forced to shut down several of its chip-fabrication factories in August temporarily. This was after the virus spread to 10,000 machines in TSMC’s most secure and advanced facilities.
Under Armour
Fitness brand Under Armour was also dealt a black eye by ransomware. Their app “MY Fitness Pal”- a portal through which users could track their diet and fitness was breached by malware.
The brand insists that the data did not contain sensitive data like social security numbers and drivers license numbers (which the app does not collect). Nor were customer payment details affected. This breach affected 150 million users.
The City of Atlanta
In March this year, the alleged creators of the SamSam ransomware launched an attack on the infrastructure of the city of Atlanta GA. The attack affected many of the city’s essential municipal functions. Among those affected were citizens’ ability to pay water bills or parking tickets.
- The ransomware demand was $51,000 (unpaid) while the recovery costs were estimated at $17 million.
- Local government in Atlanta spent over $5 million to rebuild their infrastructure after a SamSam ransomware attack in March 2018.
Industries under attack
The Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry has historically been low hanging fruit for malware. 2018 was no exception.
- Almost half of the ransomware incidents reported in 2018 involved healthcare companies. (Source: Beazley)
- 90% of healthcare organizations saw an increase in ransomware infection rates from 2017 to 2018. (Ponemon Institutes)
- 18% of healthcare devices have been the target of malware. (Source: Healthcare IT News)
- A report by CSO online estimates healthcare related malware attacks will likely quadruple by 2020.
Financial Institutions
90% of all financial institutions have experienced ransomware in the past year. (betanews.com)
These businesses have a virtual treasure trove of bank account numbers, routing numbers, and Social Security numbers that hackers can steal and later sell on the dark web.
In Q1 of 2019, Kaspersky Labs reported:
- More than 204,448 users experienced an attempt to log their banking information
- More than 280,000,000 URLs were identified as malicious
- Cybersecurity statistics show attacks were launched from within more than 190 countries
- Attacks on individuals doubled in 2018.
- Attacks on Businesses increased to one every 40 seconds.
Mobile Ransomware Threats Grow
The frightening rise of mobile malware is staggering. You may not realize that their handheld electronics are the next battlefield for domination of their personal information. In an increasingly mobile work environment, all businesses and their employees must be extra vigilant.
- Mobile malware, banking malware, and ransomware are the primary threats to expect in 2019. (Source: Fortinet)
- More than 18 million mobile malware instances were detected by Symantec in 2018. (source: Symantec)
- In Q1 2018 alone, Kaspersky Labs detected over 8,000 mobile banking ransomware Trojan installations.
- Kaspersky Labs found that the majority of the malware in 2018 was targeting phones on the Android operating system.
- Cybersecurity giant Symantec identified mobile use as a significant point of vulnerability for businesses and private users in 2018. In their annual Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR) they state “Threats in the mobile space continue to grow year-over-year, including the number of new mobile malware variants which increased by 54 %”.
- Less than 20% of mobile malware is delivered via a browser — the remainder of the payloads come through an app. (Source: RSA Current State of Cybercrime)
Protect your data and ensure business operability with phoenixNAP Ransomware Protection Solutions.
2019 Global Ransomware Predictions, By The Numbers
What are experts predicting for 2019 and beyond?
- 81 % of cybersecurity experts believe there will be a record number of ransomware attacks in 2019. (Source: CIO Dive)
- McAfee analysts suggest that individuals with a large number of connected devices and a high net worth are some of the most attractive targets.
- Attacks against Linux and Macs are expected to rise, according to IT Security Guru.
- The average costs of data breaches will reach into the hundreds of millions of dollars by 2020. (Source: Juniper Research)
- Recent studies have shown that ransomware attacks are increasing more than 300% year over year. (dimensiondata.com)
- Cybercriminals will target SaaS (Software as a Service) and cloud computing businesses, which store and secure private data. (Source: Massachusetts Institute of Technology)
- The cybersecurity research body suggests that ransomware damage costs will rise to $11.5 billion in 2019.
- Mobile malware, banking malware, and ransomware are the primary threats to expect in 2019 according to Fortinet.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) is primed to revolutionize life for businesses and consumers alike. However, the inherent vulnerability of this nascent technology can leave it wide open to ransomware attacks. A report by Kaspersky Lab indicated that new malware targeting IoT enabled devices grew threefold in 2018. Since 2017, the number of IoT focused malware attacks rose 10x from 2016.
Final Thoughts On Ransomware Statistics
As cybercriminals continue to see the value in encrypting data and restricting the access of users, different types of ransomware will continue to grow.
While newer cyber threats increase, these final stats quickly show that ransomware isn’t going away anytime soon.
50% of companies report that they do not feel as though they are adequately prepared for the threat. (healthitsecurity.com)
With damage related to cybercrime set to hit $6 trillion by 2021, investing in security spending should be a priority for 2019.