In this article you will learn:
- What a Cyber Security Attack looks like in 2020 and how to identify one.
- An attack could destroy your business overnight, a proper security defense requires understanding the offense.
- How to protect your organization from the most common cyber attack vectors. Different methods require different prevention strategies.
- In the event an attack happens, learn how to be prepared to respond and respond.
What is a Cyber Attack?
A cyber attack is an intentional exploitation of computer systems, networks, and technology-dependent enterprises. These attacks use malicious code to modify computer code, data, or logic. Culminating into destructive consequences that can compromise your data and promulgate cybercrimes such as information and identity theft. A cyber attack is also known as a computer network attack (CNA).
Common Types of Cybersecurity Attacks
Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a type of social engineering usually employed to steal user data such as credit card numbers and login credentials. It happens when an attacker, posing as a trusted individual, tricks the victim to open a text message, email, or instant message. The victim is then deceived to open a malicious link that can cause the freezing of a system as part of a ransomware attack, revealing sensitive information, or installation of malware.
This breach can have disastrous results. For an individual, this includes identity theft, stealing of funds, or unauthorized purchases.
Phishing is often used to obtain a foothold in governmental or corporate networks as part of a more significant plot such as an advanced persistent threat (APT). In such a case, employees are compromised to gain privileged access to secured data, distribute malware in a closed environment, and to bypass security parameters.
Learn more about phishing attacks.
Spear Phishing Attacks
Spear phishing is an email aimed at a particular individual or organization, desiring unauthorized access to crucial information. These hacks are not executed by random attackers but are most likely done by individuals out for trade secrets, financial gain, or military intelligence.
Spear phishing emails appear to originate from an individual within the recipient’s own organization or someone the target knows personally. Quite often, government-sponsored hacktivists and hackers perform these activities. Cybercriminals also carry out these attacks with the aim of reselling confidential data to private companies and governments. These attackers employ social engineering and individually-designed approaches to effectively personalize websites and messages.
Learn more about spear phishing attacks.
Whale Phishing Attack
A whale phishing attack is a type of phishing that centers on high-profile employees such as the CFO or CEO. It is aimed at stealing vital information since those holding higher positions in a company have unlimited access to sensitive information. Most whaling instances manipulate the victim into permitting high-worth wire transfers to the attacker.
The term whaling signifies the size of the attack, and whales are targeted depending on their position within the organization. Since they are highly targeted, whaling attacks are more difficult to notice compared to the standard phishing attacks.
In a business, system security administrators can lessen the effectiveness of such a hack by encouraging the corporate management staff to attend security awareness training.

Malware Attacks
Malware is a code that is made to stealthily affect a compromised computer system without the consent of the user. This broad definition includes many particular types of malevolent software (malware) such as spyware, ransomware, command, and control.
Many well-known businesses, states, and criminal actors have been implicated of and discovered deploying malware.
Malware differs from other software in that it can spread across a network, cause changes and damage, remain undetectable, and be persistent in the infected system. It can destroy a network and bring a machine’s performance to its knees.
Ransomware
Ransomware blocks access to a victims data, typically threating delete it if a ransom is paid. There is no guarantee that paying a ransom will regain access to the data. Ransomware is often carried out via a Trojan delivering a payload disguised as a legitimate file.
Learn more about ransomware attacks and how to prevent them.
Drive-by Attack
A drive-by attack is a common method of distributing malware.
A cyber attacker looks for an insecure website and plants a malicious script into PHP or HTTP in one of the pages. This script can install malware into the computer that visits this website or become an IFRAME that redirects the victim’s browser into a site controlled by the attacker. In most cases, these scripts are obfuscated, and this makes the code to be complicated to analyze by security researchers. These attacks are known as drive-by because they don’t require any action on the victim’s part except visiting the compromised website. When they visit the compromised site, they automatically and silently become infected if their computer is vulnerable to the malware, especially if they have not applied security updates to their applications.
Trojan Horses
A Trojan is a malicious software program that misrepresents itself to appear useful. They spread by looking like routine software and persuading a victim to install. Trojans are considered among the most dangerous type of all malware, as they are often designed to steal financial information.

Web Attacks
SQL Injection
SQL injection, also known as SQLI, is a kind of attack that employs malicious code to manipulate backend databases to access information that was not intended for display. This may include numerous items including private customer details, user lists, or sensitive company data.
SQLI can have devastating effects on a business. A successful SQLI attack can cause deletion of entire tables, unauthorized viewing of user lists, and in some cases, the attacker can gain administrative access to a database. These can be highly detrimental to a business. When calculating the probable cost of SQLI, you need to consider the loss of customer trust in case personal information like addresses, credit card details, and phone numbers are stolen.
Although SQLI can be used to attack any SQL database, the culprits often target websites.
Cross Site Scripting
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a kind of injection breach where the attacker sends malicious scripts into content from otherwise reputable websites. It happens when a dubious source is allowed to attach its own code into web applications, and the malicious code is bundled together with dynamic content that is then sent to the victim’s browser.
Malicious code is usually sent in the form of pieces of Javascript code executed by the target’s browser. The exploits can include malicious executable scripts in many languages including Flash, HTML, Java, and Ajax. XSS attacks can be very devastating, however, alleviating the vulnerabilities that enable these attacks is relatively simple.
Other Types of Cyber Security Threats
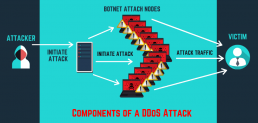
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack?
Denial-of-service (DDoS) aims at shutting down a network or service, causing it to be inaccessible to its intended users. The attacks accomplish this mission by overwhelming the target with traffic or flooding it with information that triggers a crash. In both situations, the DoS onslaught denies legitimate users such as employees, account holders, and members of the resource or service they expected.
DDoS attacks are often targeted at web servers of high-profile organizations such as trade organizations and government, media companies, commerce, and banking. Although these attacks don’t result in the loss or theft of vital information or other assets, they can cost a victim lots of money and time to mitigate. DDoS is often used in combination to distract from other network attacks.
Learn more about DDoS Attacks.
Password Attack
A password attack simply means an attempt to decrypt or obtain a user’s password with illegal intentions.
Crackers can use password sniffers, dictionary attacks, and cracking programs in password attacks. There are few defense mechanisms against password attacks, but usually, the remedy is inculcating a password policy that includes a minimum length, frequent changes, and unrecognizable words.
Password attacks are often carried out by recovering passwords stored or exported through a computer system. The password recovery is usually done by continuously guessing the password through a computer algorithm. The computer tries several combinations until it successfully discovers the password.
Eavesdropping Attack
Eavesdropping attacks start with the interception of network traffic.
An Eavesdropping breach, also known as snooping or sniffing, is a network security attack where an individual tries to steal the information that smartphones, computers and other digital devices send or receive This hack capitalizes on unsecured network transmissions to access the data being transmitted. Eavesdropping is challenging to detect since it doesn’t cause abnormal data transmissions.
These attacks target weakened transmissions between the client and server that enables the attacker to receive network transmissions. An attacker can install network monitors such as sniffers on a server or computer to perform an eavesdropping attack and intercept data as it is being transmitted. Any device within the transmitting and receiving network is a vulnerability point, including the terminal and initial devices themselves. One way to protect against these attacks is knowing what devices are connected to a particular network and what software is run on these devices.
Birthday attack
The birthday attack is a statistical phenomenon that simplifies the brute-forcing of one-way hashes. It is based on the birthday paradox that states that for a 50 percent chance that someone shares your birthday in any room, you need 253 individuals in the room. However, for a chance higher than 50 percent, you only require 23 people. This probability works because these matches depend on pairs. If you choose yourself as one of the pairs, you only need 253 people to get the required number of 253 pairs. However, if you just need matches that don’t include you, you only need 23 people to create 253 pairs when cross-matching with each other. Thus, 253 is the number you need to acquire a 50 percent probability of a birthday match in a room.
Brute-Force and Dictionary Network Attacks
Dictionary and brute-force attacks are networking attacks whereby the attacker attempts to log into a user’s account by systematically checking and trying all possible passwords until finding the correct one.
The simplest method to attack is through the front door since you must have a way of logging in. If you have the required credentials, you can gain entry as a regular user without creating suspicious logs, needing an unpatched entry, or tripping IDS signatures. If you have a system’s credentials, your life is even simplified since attackers don’t have these luxuries.
The term brute-force means overpowering the system through repetition. When hacking passwords, brute force requires dictionary software that combines dictionary words with thousands of different variations. It is a slower and less glamorous process. These attacks start with simple letters such as “a” and then move to full words such as “snoop” or “snoopy.”
Brute-force dictionary attacks can make 100 to 1000 attempts per minute. After several hours or days, brute-force attacks can eventually crack any password. Brute force attacks reiterate the importance of password best practices, especially on critical resources such as network switches, routers, and servers.
Learn more about Brute Force attacks.
Insider Threats
Not every network attack is performed by someone outside an organization.
Inside attacks are malicious attacks performed on a computer system or network by an individual authorized to access the system. Insiders that carry out these attacks have the edge over external attackers since they have authorized system access. They may also understand the system policies and network architecture. Furthermore, there is less security against insider attacks since most organizations focus on defending against external attacks.
Insider threats can affect all elements of computer security and range from injecting Trojan viruses to stealing sensitive data from a network or system. The attackers may also affect the system availability by overloading the network or computer processing capacity or computer storage, resulting in system crashes.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks are a type of cybersecurity breach that allows an attacker to eavesdrop a communication between two entities. The attack occurs between two legitimate communicating parties, enabling the attacker to intercept communication they should otherwise not be able to access. Thus the name “man-in-the-middle.” The attacker “listens” to the conversation by intercepting the public key message transmission and retransmits the message while interchanging the requested key with his own.
The two parties seem to communicate as usual, without knowing the message sender is an unknown perpetrator trying to modify and access the message before it is transmitted to the receiver. Thus, the intruder controls the whole communication.
AI-Powered Attacks
The concept of a computer program learning by itself, building knowledge, and getting more sophisticated may be scary.
Artificial intelligence can be easily dismissed as another tech buzzword. However, it is already being employed in everyday applications through an algorithmic process referred to as machine learning. Machine learning software is aimed at training a computer to perform particular tasks on its own. They are taught to accomplish tasks by doing them repeatedly while learning about certain obstacles that could hinder them.
AI can be used to hack into many systems including autonomous vehicles and drones, converting them into potential weapons. AI makes cyber attacks such as identity theft, password cracking, and denial-of-service attacks, automated, more powerful and efficient. It can also be used to kill or injure people, steal money, or cause emotional harm. Larger attacks can as well be used to affect national security, shut down hospitals, and cut power supplies to entire regions.
Be Prepared For Attacks On Your Network
This article has reviewed the top cyber-security attacks that hackers use to disrupt and compromise information systems.
For you to mount a good defense mechanism, you need to understand the offense. This review of the most common cyber attacks shows you that attackers have many options while choosing attacks to compromise and disrupt information systems. You also need to be proactive in defending and securing your network.
Maintain an updated antivirus database, train your employees, keep your passwords strong, and use a low-privilege IT environment model to protect yourself against cyber attacks.