Enterprise Password Management
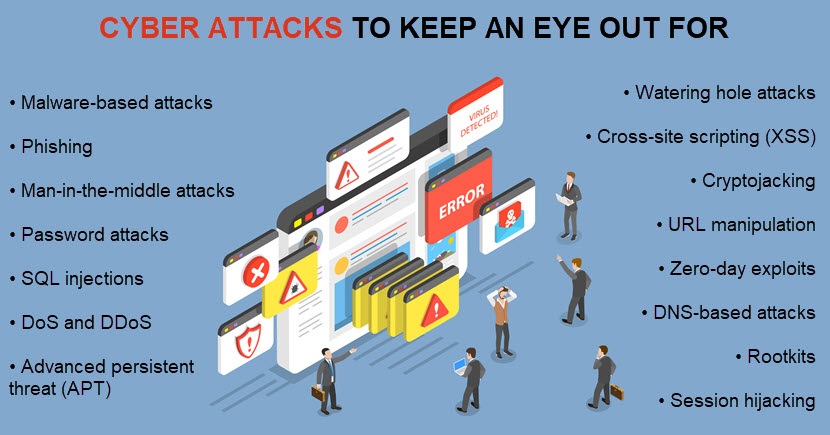
Almost 81% of hacking-related data breaches involve either a weak or stolen employee password. How an organization manages and protects credentials is critical to cybersecurity, which is why a growing number of companies are investing time and funds into enterprise password management.
This article is a complete guide to enterprise password management (EPM). We explain the basics of EPM, present go-to strategies and best practices, plus offer detailed reviews of the 12 best EPM tools currently available on the market.

Our guide to strong passwords explains how to create credentials that are easy to remember and impossible to crack. You can also use PNAP's Password Generator to create a unique password instantly.
What Is Enterprise Password Management (EPM)?
Enterprise Password Management (EPM) is a set of policies and tools organizations use to manage, protect, and control access to authentication credentials. EPM enables companies to:
- Define, centrally manage, and enforce company-wide password policies.
- Ensure employees use strong and unique passwords for every account.
- Automate various password-related tasks (creation, sharing, resets, syncs, etc.).
- Monitor and audit password usage across the organization.
The goal of EPM is to keep passwords safe without overly inconveniencing the workforce. An EPM tool must ensure security, but also provide a simple way to create, store, and access passwords.
The core feature of all EPM tools is so-called password vaulting. Each employee gets a personalized virtual "locker" for storing credentials. Users access the vault with a master key, which is the only password employees must remember. Once you log into the vault, the tool provides access to all other credentials.
Here's a list of other common features you should expect from an average EPM tool:
- The ability to control and enforce password-related rules (e.g., complexity requirements and expiration periods).
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Synchronization of usernames and passwords across multiple devices.
- Reports on how employees use passwords.
- Auto-filling of forms.
- Automatic credential resets.
- Prevention of suspicious log-ins.
In addition to improving the security posture, enterprise password management also helps meet compliance requirements. Many industry and regulatory standards (PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.) insist on tight control over user and employee credentials.
Interested in learning about compliance? Here are a few helpful reads:
Why Is Enterprise Password Management Important?
Here's why implementing enterprise password management should be at the top of a company's to-do list:
- Keep sensitive data and systems safe: Passwords are the most common way of authenticating employees accessing files and systems. High levels of EPM ensure everyone uses strong and unique passwords, lowering the likelihood of intruders reaching valuable data and assets.
- Enforce company-wide policies: An EPM platform enables you to set password-related policies. You control the minimum length and complexity for each password, plus ensure no one reuses the same credentials for different accounts or services.
- Counter password-based attacks: Strong credentials are the most effective way of countering password-based attacks. You lower the risk of successful brute force, dictionary, and spraying attacks.
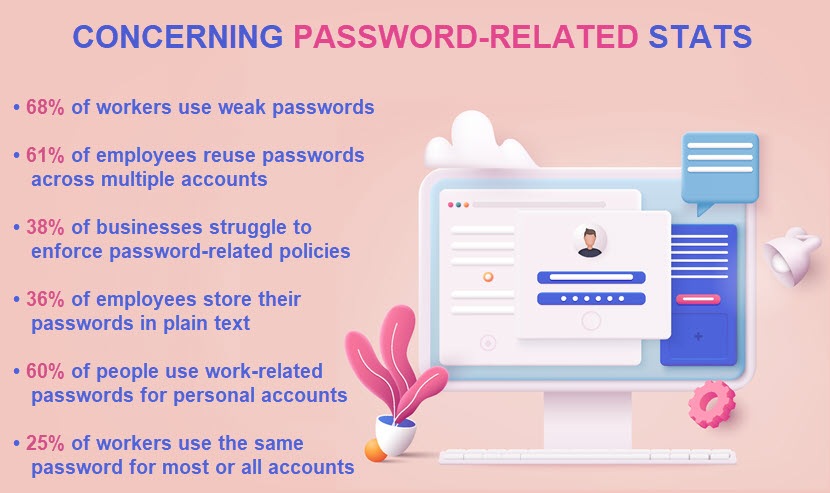
- Take the burden off employees: An average employee has 27 work-related passwords, which is the main reason why people reuse credentials and create easy-to-remember passwords. An EPM tool takes away the burden of having to remember credentials for each account, making it easier for employees to use unique, complex passwords.
- Lower risk of human error: An EPM tool helps prevent errors that lead to a compromised password. For example, a tool helps recognize fake phishing websites that ask for login info and prevents employees from storing and sharing passwords in plain text files.
- Boost team productivity: A password manager makes it significantly easier for employees to create and use passwords. Teams spend less time on password-related tasks and access resources with more speed.
- Monitor password usage: EPM platforms track how employees use, store, and share passwords. Such oversight boosts security and helps identify vulnerabilities you can address with training sessions and policy updates.
Recent studies reveal that between 20% and 50% of all help desk calls are for password resets (a process that takes 2-30 minutes to complete depending on what went wrong and general tech-savviness). The average cost of each reset is $70, so EPM tools also reduces day-to-day costs for your organization.
Enterprise Password Management Best Practices
Here's a list of the best practices for managing, storing, and protecting passwords (with or without an EPM tool):
- Enforce the use of strong passwords with rules for minimum length (at least 12 characters long) and complexity requirements (a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, punctuation, and special symbols).
- Ensure every employee changes their password regularly, either biweekly or monthly (and without reverting to a previously used password).
- Never use the same password for different accounts or services.
- Ensure employees do not store or share passwords in plain-text files.
- Use multi-factor authentication to require employees to provide additional verification beyond their password (e.g., a token on a mobile device or a biometric scan).
- Lock accounts after 3-5 unsuccessful password guesses (a leading brute force prevention measure).
- Conduct regular audits of password-related policies, procedures, and usage rules.
- Keep all EPM software up to date with the latest patches.
- Change default passwords before deploying new software.
- Ensure employees know how to use and make the most out of password vaults.
- Monitor for suspicious login attempts (e.g., someone logging in in the middle of the night or from a different state).
- Use at-rest encryption and in-transit encryption to keep passwords safe.
- Organize regular training to ensure everyone is up to date with the latest password-related threats and rules.
Check out our article on security awareness training to get tips on making your sessions as streamlined and effective as possible.
12 Best Enterprise Password Management Solutions
Below is an in-depth look at the best enterprise password management tools currently on the market. We reviewed both free and paid platforms, so you'll find the right fit regardless of your budget.
Free Enterprise Password Management Solutions
Let's first check out the best EPM tools that offer enough "freemium" features to significantly improve password management and security at your organization.

KeePass
KeePass is an open-source password management tool that relies on AES 256-bit encryption with plugins that support additional algorithms (GOST, Twofish, ChaCha20, and Serpent).
Despite being completely free, KeePass is rich in features. Here's an overview of what the tool offers:
- The ability to store all your passwords in one database locked with a master key.
- Encryption of the complete vault, not only the password fields.
- Password edit controls.
- The freedom to use either a master password or a key file (or combine both methods).
- A feature for exporting the password list to various formats (TXT, HTML, XML, and CSV).
- Simple database transfers and imports from other password managers.
- The ability to create, modify, and delete password groups.
- Time fields (creation, last modification, last access, and expiration times).
- Multi-factor authentication.
- Auto-type capability.
- A strong password generator.
KeePass also enables you to write custom plug-ins (or download plug-ins from other users) to extend the tool's functionality.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, and Linux (there are unofficial editions for Android, iOS, and all major browsers).
Who should use it: Companies on the market for a free EPM tool and with teams experienced in open-source coding.
Main pros of KeePass
- The tool is completely free and open source (OSI certified).
- Compatible with most operating systems, browsers, and smart devices thanks to various unofficial versions of the tool.
- High levels of security.
- Very customizable.
- Has a portable version you carry on an external device and just plug in without installation.
Main cons of KeePass
- A steep learning curve for less tech-savvy users.
- An outdated interface.
- No live user support, so users must rely on community forums for help.

Bitwarden
Bitwarden is an open-source password manager that uses AES-CBC 256-bit encryption for vaults and PBKDF2 SHA-256 for encryption keys. Unlike KeePass, Bitwarden has both a free and paid edition.
The main trait behind Bitwarden's security is that the tool does not store your passwords. Instead, the platform keeps encrypted versions of passwords, and users are the only ones with the decryption key.
Bitwarden's free tier is limited compared to the paid version of the tool, but the free edition offers a well-rounded set of features:
- Free to use across multiple devices.
- Data breach reports.
- Multiple logins for the same applications.
- Storage for unlimited passwords on an unlimited number of synced devices.
- Auto-fill and auto-capture capabilities.
- One gigabyte of available storage.
- Two-factor authentication.
- Simple password sharing.
- The option to use a physical security key.
Bitwarden's Teams edition costs $3/month per user and the Enterprise tier charges $5/month per user. Premium versions of the tool provide extra features, such as 2FA via YubiKey and FIDO2, priority support, custom management roles, and single sign-on (SSO).
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, Opera, Vivaldi, Brave, DuckDuck Go, and Tor).
Who should use it: Smaller, tech-savvy teams looking for a free or low-cost EPM tool.
Main pros of Bitwarden
- An open-source tool.
- The free version allows unlimited vault items across unlimited synced devices.
- Only keeps encrypted versions of passwords.
- An intuitive, easy-to-use interface.
- A track record of quickly detecting and updating errors (mainly due to the tool's bug bounty program).
Main cons of Bitwarden
- Limited customer support for the free version of the tool.
- No dark web monitoring or biometric 2FA for any version of the tool.
- The Send feature enables users to share passwords insecurely.

Norton Password Manager
Norton Password Manager is one of the most streamlined free password managers on the market. The tool provides users with:
- Highly secure password vaults protected with 256-bit AES encryption and TLS secure connections.
- Basic two-factor authentication (including biometric login for mobile users).
- A zero-knowledge policy.
- Unlimited password storage.
- A Safety Dashboard that helps track accounts, make updates, and prevent duplicate or weak passwords.
- Vault auditor.
- Automatic password changer.
Norton also offers a free password generator that helps quickly and easily create hard-to-crack credentials.
Compatibility: Android and iOS (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge).
Who should use it: Sole proprietors and small businesses looking for a free and easy-to-use password manager.
Main pros of Norton Password Manager
- The tool is completely free and does not "lock" any features behind a premium edition.
- Stores an unlimited number of passwords.
- A sleek, easy-to-navigate interface.
- Creates strong passwords automatically.
- Syncs accounts across multiple devices.
Main cons of Norton Password Manager
- Does not allow users to share passwords one-on-one.
- Lackluster documentation.
- Can't set up multiple users under the same account.

Dashlane
Dashlane is a password manager that has both free and paid editions. The main selling point of this tool is its high levels of safety as Dashlane uses the following measures to keep vaults safe:
- End-to-end AES-256 encryption.
- A zero-knowledge architecture.
- Both 2FA and universal 2FA verification.
- A built-in VPN.
The free version of Dashlane offers the following features:
- Storage of up to 50 passwords (available for up to 5 accounts).
- Password sharing for up to 5 accounts.
- A password generator.
- Health checker that searches for weak, reused, and compromised passwords.
- Form auto-fill.
- Alerts in case of incidents.
- Biometric account recovery.
Paid versions of Dashlane (which start at $4.99/month per user) include extra features, such as:
- Dark web monitoring.
- Unlimited password sharing.
- 1GB of encrypted file storage.
- An excellent dashboard that helps pinpoint password-related problems and monitor usage.
- Enforceable policy settings.
- Advanced account monitoring and reporting.
- SSO options.
- Active Directory integration.
- Remote account deletion.
High levels of security and a built-in VPN make Dashlane a sound choice for companies with remote-first workforces.
Compatibility: Windows, MacOS, iOS, and Android (plus extensions for Edge, Chrome, Firefox, and Safari).
Who should use it: Companies that rely on remote teams and are worried about login security.
Main pros of Dashlane
- Easy to set up and use.
- High levels of cybersecurity.
- Unlimited password storage and device syncing for all editions of the tool.
- A powerful and easy-to-use admin console.
- Detailed reporting.
Main cons of Dashlane
- The free plan limits users to one device.
- Too many features locked behind a "paywall."
Learn about shadow IT and see why the use of unsanctioned devices is a common cause of password-related incidents.
Paid Enterprise Password Management Solutions
Let's now explore the market's top paid enterprise password management tools that offer the most value for your money.

1Password
1Password is a popular password manager with a range of excellent EPM features, such as:
- Creation of multiple vaults to store passwords, credit card data, API tokens, etc.
- Customizable controls with granular-access features (permissions by category, group, role, etc.).
- Creation of temporary guest credentials with flexible expiration options (one view, one hour, one day, 7 days, 14 days, or 30 days).
- The Watchtower feature that monitors for reused passwords, vulnerable credentials, and compromised accounts.
- Integration with identity and access management (IAM) platforms (Okta, Active Directory, and Rippling).
- Detailed health reporting.
- Biometric login options and multi-factor authentication using Duo.
This EPM tool has a detailed knowledge base that helps users set up and use the tool. 1Password also integrates with Have I Been Pwned to monitor for data breaches.
1Password Business tier pricing is $7.99/month per user, but there's also the Team Starter Pack option that costs $19.95/month for up to 10 users. The tool has a 14-day free trial for all plans.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Brave, and Safari).
Who should use it: SMBs that want granular password controls and in-depth monitoring.
Main pros of 1Password
- Excellent admin dashboards.
- Proactively helps employees maintain good password hygiene.
- Encrypts passwords both at rest and in transit.
- Granular security controls.
- An unlimited number of users and passwords.
- A bonus Family plan for every Business user.
Main cons of 1Password
- Only allows 20 guest accounts at one time.
- Expensive for larger teams.
- Limited import options.

NordPass
NordPass is an excellent tool that encodes all sensitive data with the xChaCha20 encryption protocol. Other security-related capabilities offered by the tool include:
- Mandatory multi-factor authentication.
- The capability to identify weak, reused, and old passwords.
- A data breach scanner that monitors the web for leaked data.
- Guaranteed GDPR and HIPAA compliance.
Additionally, NordPass keeps user activity logs that enable an organization to track password usage and overall health. You also get cross-platform support, auto-fill capabilities, and the ability to store different types of credentials.
NordPass Business tier pricing starts from $3.59/month per employee (up to 250 users). The Enterprise edition allows more than 250 users, plus has SSO with Azure AD, MS ADFS, and Okta. Both tiers have trial periods.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Opera).
Who should use it: Organizations chiefly worried about data security compliance rules (e.g., healthcare providers or companies operating in the E.U.).
Main pros of NordPass
- Unlimited users and password storage.
- A complete overview of password-related activities.
- Premium 24/7 customer support.
- Easy user management.
- Quick and secure group password sharing.
- Detailed user activity logs.
- Actionable password health report.
Main cons of NordPass
- The Business plan does not support SSO.
- Unknown prices for the Enterprise tier.
- You cannot use the free version of the tool on multiple devices simultaneously.

LastPass
LastPass is a password manager that uses AES 256-bit encryption and operates under a zero-knowledge policy. The tool is also SOC2, SOC3, C5, ISO27001, and GDPR compliant.
LastPass's main selling point is its ease of use. The tool is very simple and convenient for employees as it enables them to easily:
- Create, store, and organize passwords.
- Perform one-to-one password sharing.
- Access work apps from anywhere and any device.
- Use the SSO feature and enable multiple platform sign-ins with a single ID.
- Use auto-fill to speed up logins.
- Go "passwordless" and get seamless access to vaults.
LastPass also emphasizes proactive security with features such as:
- Immediate alerts if a company or personal data is at risk.
- Over 100 customizable policies for personalizing security rules.
- Reports on employee password management behavior.
- Dark web monitoring.
LastPass has two tiers: the Teams edition (which costs $4.25/month per user) and the Business edition (which charges $6.25/month per user). The Teams tier limits you to under 50 users, while the Business version has no user cap. Both tiers have a trial period.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Opera).
Who should use it: Teams looking for an easy-to-use password manager with well-rounded features.
Main pros of LastPass
- Unlimited passwords.
- Emphasizes user convenience.
- Over 100 customizable policies.
- In-depth admin security reports.
- Over 1,200 pre-integrated SSO apps.
- Extra free Family package licenses for each employee.
Main cons of LastPass
- The Teams tier has a limit of only 50 users.
- Only gives 3 SSO apps with MFA and requires an extra $2/month per seat for more.
- While the company bounced back, LastPass suffered a concerning data breach in August 2022.

Zoho Vault
Zoho Vault is an affordable password manager that comes in several editions. Even the free version is okay for individual users, but the Team tier (which charges $0.90/month per user) has solid EPM features, including:
- Dedicated password vaults for teams (protected with the AES 256-bit cipher).
- Centralized admin controls.
- Multi-factor authentication.
- Simplified sign-ins and password sharing.
- Password policy enforcement.
- Credential expiration alerts.
- IP address restrictions.
- Password imports from browsers.
- Integration with G Suite and Office 365.
The more feature-rich Enterprise edition charges a minimum of $4.50/month per user and adds additional capabilities, such as:
- User group management.
- A "break glass" account for emergency access.
- SSO for cloud apps.
- Custom alerts for password-related events.
- Detailed reports on user access, sharing behavior, and general password hygiene.
- Integration with Okta and OneLogin.
- Helpdesk integration.
Zoho also offers a range of other business apps (such as CRM and sales software), all of which integrate seamlessly with Zoho Vault.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, Brave, and Vivaldi).
Who should use it: Companies on the market for feature-rich and affordable EPM services.
Main pros of Zoho Vault
- The Team tier is among the most affordable EPM solutions on the market, yet still has decent features.
- Advanced 256-bit encryption and zero-knowledge architecture.
- In-depth password security reports.
- Great transparency of password usage.
- Integration with other Zoho solutions.
- Syncs across Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS devices.
Main cons of Zoho Vault
- Monthly subscriptions are considerably more expensive than yearly plans.
- Users cannot import saved Safari passwords.
- Weekday-only 24h support.

Passbolt
Passbolt is an open-source password manager known for its flexibility and customization. The tool's Community tier is free to use for an unlimited number of users and has the following features:
- Passwords management and sharing.
- Private and shared folders.
- User and group management.
- Two-factor and 3-step authentication.
- Open API.
The Business tier (which costs $3/month per user) adds the following features:
- LDAP provisioning.
- Account recovery (escrow).
- Tags management.
- Activity logs for tracking changes.
- SSO with Microsoft.
Finally, the Enterprise tier (which has custom prices) offers additional features you won't find in many other EPM tools, such as:
- High availability consulting.
- Disaster recovery consulting.
- White glove migration.
- Custom features development.
Passbolt enables users to choose whether to self-host the tool on their servers or use the platform's cloud services.
Compatibility: The team behind Passbolt recommends you run the tool on a stable version of a major Linux distribution, such as Debian or Ubuntu. There are browser extensions for Edge, Chrome, and Firefox.
Who should use it: Organizations with teams experienced in open-source tools and looking to host an EPM on an in-house server.
Main pros of Passbolt
- Open source (under AGPLV3 license).
- A rich selection of features, some of which are rare in the EPM niche.
- A flexible number of users for the Business tier.
- Highly customizable and extensible thanks to its restful API.
- The freedom to choose whether you want to host the tool on-prem or in the cloud.
Main cons of Passbolt
- No mobile or desktop apps.
- Doesn't support advanced logs for audits.
- The Enterprise tier does not have transparent prices.

Keeper
Keeper is a password management tool that offers top-tier security and EPM services. The tool is highly secure thanks to a zero-trust and zero-knowledge architecture.
Keeper has three paid tiers, all of which allow an unlimited number of devices. The Starter plan (which costs $2.00/month per user) offers:
- Encrypted vault for every user (for passwords and other files).
- Folders and subfolders (shared and personal).
- Policy enforcement.
- Security audits and activity reporting.
- Team management.
- Two-factor authentication.
The Business tier (which costs $3.75/month per user) adds delegated administration, share admins, and advanced organizational structure. Finally, the Enterprise edition (which has custom prices) adds advanced features like:
- SSO (SAML 2.0) authentication.
- Automation features.
- AD and LDAP syncs.
- SCIM and CLI provisioning.
- Developer APIs.
- Dark web protection.
- Advanced reporting.
All tiers have access to a helpful password generator that enables users to quickly create strong and unique credentials.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Brave, Safari, Edge, and Opera).
Who should use it: Sizable companies looking for advanced EPM services and good per-user prices.
Main pros of Keeper
- Highly secure and rich with features.
- Very customizable.
- Excellent UI/UX.
- Free family plan for every user.
- Smooth password capture and replay.
- Multiple forms of MFA.
Main cons of Keeper
- You need a skilled in-house team to make the most out of the tool.
- Unknown prices for the Enterprise tier.
- Relatively small storage limits.

Roboform
RoboForm is an excellent password manager that excels at enforcing EPM rules at larger companies thanks to:
- Centralized employee onboarding and company-wide policy deployment features.
- An unlimited number of admins.
- The capability to easily monitor and customize access to passwords based on employee roles.
- Excellent SSO support.
- Highly customizable policies.
This EPM tool enables users to store various data in their vaults (passwords, usernames, bookmarks, business-related files, etc.). All stored data is easily sharable across teams.
Teams with 1 to 10 members will have to pay $39.95/year per user for RoboForm. The tool does have 3-year and 5-year subscription options that bring the per-user price down, plus larger teams get significant discounts.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Opera).
Who should use it: Bigger companies looking for top-tier EPM for large teams spread across multiple departments.
Main pros of Roboform
- End-to-end AES256-bit encryption for password creation, storing, and sharing.
- The tool decrypts data locally.
- Enables companies to easily manage large numbers of people.
- Intuitive and easy-to-use password automation.
- Excellent onboarding and training materials.
- Detailed knowledge base and 24/7/365 support.
Main cons of Roboform
- On the expensive side for smaller teams.
- Clients outside the USA occasionally have problems getting quick tech support.
- Limited importing options.

Sticky Password
Sticky Passwords is a cost-friendly password manager with a solid offering that includes:
- Simple and safe password sharing.
- 2FA.
- Auto-fill capabilities.
- Customizable permissions.
- A built-in password generator.
- Various syncing options.
- USB password vaults (so-called Portable Passwords).
One of Sticky Password's main selling points is that the tool guarantees clients never permanently lose employees' credentials. In case of an incident or a disgruntled employee, there's an Emergency Access feature that allows admins to gain access to a specific account.
Sticky Password charges clients $29.99/year per user. The tool has a free edition, but that version of Sticky Password does not allow syncing or password sharing. There is also the premium version that charges $39.99/year per user and adds syncing across devices and dark web monitoring.
Compatibility: Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android (plus extensions for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, Opera, and Brave).
Who should use it: Less tech-savvy teams with many shared machines that wish to ensure there's no way to permanently lose credentials.
Main pros of Sticky Passwords
- Simple to use and cost-effective.
- Users can use a flash drive as a plug-and-play password management device.
- A helpful Emergency Access feature.
- Excellent form filling.
- Each license includes a donation to save endangered manatees.
Main cons of Sticky Passwords
- The Premium version does not add enough features to justify the price difference.
- No password inheritance.
- If you forget your master password, the account is gone for good.

Which Enterprise Password Management Solution Should You Choose?
The first decision you must make is whether you'll use a free or paid enterprise password management tool. Most platforms keep advanced features behind a "paywall," but basic features are enough for some companies and use cases.
If you opt for a paid EPM tool, remember to both consider the initial purchase and ongoing maintenance costs. Other factors you must account for when choosing a tool are:
- Specific security features offered by the tool (e.g., end-to-end encryption or MFA).
- How much you'll have to customize the tool.
- Any relevant compliance requirements.
- Your in-house team's preference and previous experience.
- Whether the tool will be able to scale alongside your needs without impacting performance.
- Integrations with existing IT infrastructure and systems.
- The level of required customer support.
- How much time the tool requires for day-to-day maintenance.
Consider these factors and go with one of the enterprise password management tools discussed above. Every tool we covered here is a worthwhile choice, but some fit certain use cases better than others.
We also recommend you test the tool before going all-in on a paid edition. All the platforms discussed above have some form of trial, so there's no harm in giving several tools a go and seeing which one performs the best before choosing a long-term solution.
Free or Paid, an EPM Tool is a Must
Manual management of your company's passwords is too complex, time-consuming, and outright risky. Even a single password falling into the wrong hands is enough to cause a data leakage or breach, so invest in EPM and ensure your credentials are safe from prying eyes.